How do planes fly?
The fundamental reason planes can fly lies in the lifting force that counteracts the gravitational pull. There are two main concepts of buoyancy that explain how this force is achieved.
Static buoyancy
First, we have the static buoyancy, the principle behind objects floating in a fluid. If an object has a lower density than the surrounding fluid, it will float.
For instance, a helium ballon with rises because helium is less dense than air, and the weight of the displaced air is greater than the weight of the helium-ballon. However, static buoyancy is not sufficient for lifting heavy objects like planes made of dense materials.
Dynamic buoyancy
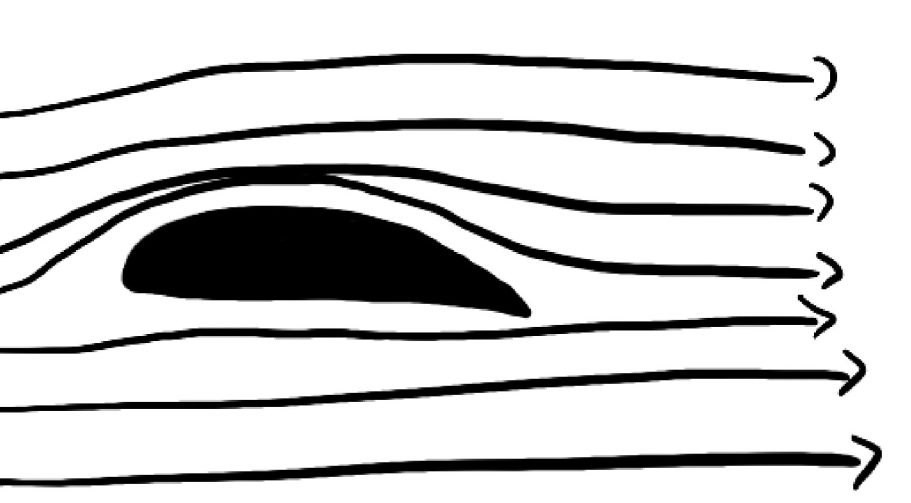
This brings us to the the dynamic buoyancy, or aerodynamic lift. Air flows along the wings of the plane while flying and the wing of a plane is designed to deflect air downwards as it moves through the atmosphere. This causes a reaction force that pushes the wing upwards, according to Newton’s third law. The wing splits the airflow into two streams- one flowing over the top and own flowing beneath. The air above the wing moves faster, creating a region of lower pressure, while the air beneath moves slower, resulting in higher pressure.
This pressure difference generates lift, which allows the plane to overcome gravity.
©Copyright. All rights reserved.
Wir benötigen Ihre Zustimmung zum Laden der Übersetzungen
Wir nutzen einen Drittanbieter-Service, um den Inhalt der Website zu übersetzen, der möglicherweise Daten über Ihre Aktivitäten sammelt. Bitte überprüfen Sie die Details in der Datenschutzerklärung und akzeptieren Sie den Dienst, um die Übersetzungen zu sehen.